When we build a model via the Designer and build it on a Cloudlet, Livebase generates the corresponding database based on the following rules:
- One table is generated for each class;
- One-to-many or many-to-one associations are rendered with a foreign key in the “many-to-many” table, pointing to the “one-to-one” table;
- one-to-one associations are rendered with a foreign key in either table, depending on the navigability of the association;
- Many-to-many associations are rendered with an additional table, referred to as a relationship table. It has two foreign keys to the tables involved, and its records are the identifiers of the instances between which the association exists;
- compositions are rendered with a foreign key in the table of the part class, to that of the whole class;
- Minimum and maximum cardinality constraints cannot be expressed in the database: they are verified only at the application level;
- In general, the navigability of an association can influence whether and how it can be translated in the database.
Let’s make this clearer with a series of examples. In all of them we will assume two classes ClassA and ClassB with roles RoleA and RoleB respectively, connected by associations of various types. In the images accompanying the above examples, we will indicate the columns on which a not null constraint is defined in bold, and those for which a unique constraint is defined in cursive. Finally, in the expressions of the minimum and maximum cardinality constraints we will make use of the variables n and N to indicate arbitrary values, with N>n>0.
One-to-many/many-to-one associations #
If the cardinality of RoleA is 01 and that of RoleB is 0N (* in Designer), regardless of navigability…
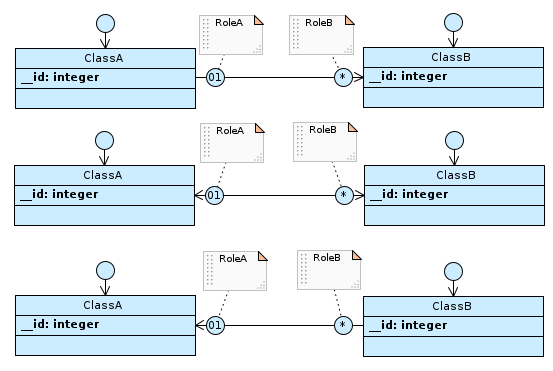
…in the ClassB table, the foreign key to ClassA will always be present.
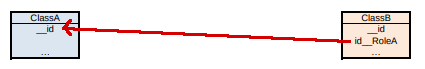
If the cardinality of RoleA is 1 and that of RoleB is 0N (* in Designer), and the association is navigable from ClassB to ClassA or both ways…
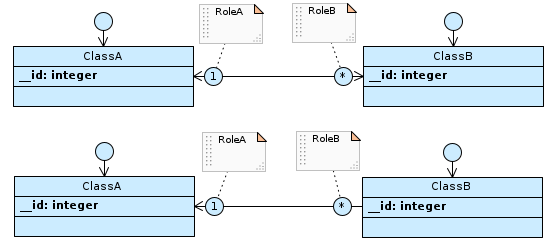
…table ClassB has the foreign key to ClassA, with the not null constraint.
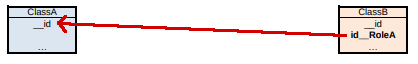
If the cardinality of RoleA is 01 and that of RoleB is nN (C in Designer), and the association is navigable from ClassA to ClassB or both ways…
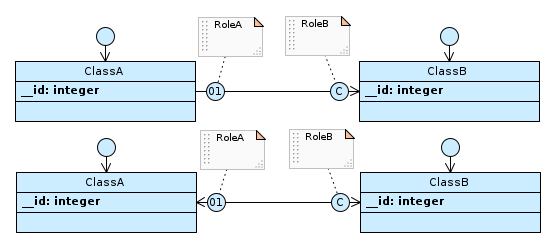
…table ClassB has the foreign key to ClassA.
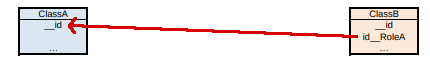
One-to-many/many-to-one : modeling not allowed #
Since RoleB is not accessible, the following associations cannot be modeled, because the navigability conditions do not allow the creation of instances of ClassA:
- associations where the cardinality of
RoleAis01and that ofRoleBisnN(Cin the Designer), navigable fromClassBtoClassA.
Since RoleA is not accessible, the following associations cannot be modeled, because the navigability conditions do not allow instances of ClassB to be created:
- associations where the cardinality of
RoleAis1and that ofRoleBis0N(*in Designer), navigable fromClassAtoClassBor both ways.
The following associations cannot be modeled due to the egg-chicken problem between ClassA and ClassB. It is not possible to define an instance of one in the absence of at least one instance of the other:
- associations where the cardinality of
RoleAis1and that ofRoleBisnN(Cin Designer), regardless of navigability.
One-to-one associations #
If the cardinality of RoleA is 01 and that of RoleB is 01, and the association is navigable from ClassA to ClassB or both…
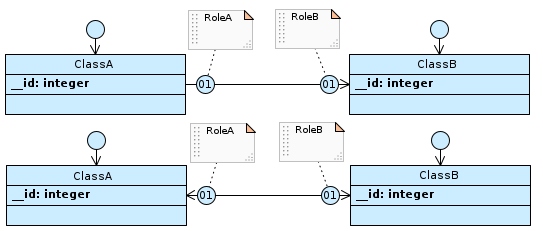
…table ClassA has the foreign key to ClassB, with a uniqueness constraint defined.
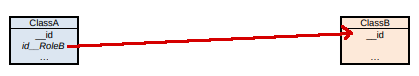
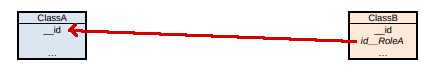
If the association is only navigable from ClassB to ClassA…
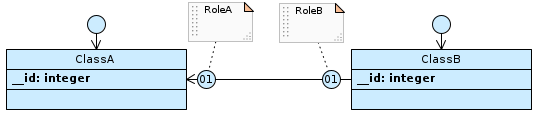
…it will be ClassB that has the foreign key to ClassA, with the unique constraint defined.
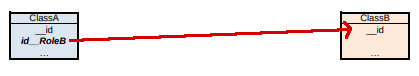
If the cardinality of RoleA is 01 and that of RoleB is 1, and the association is navigable from ClassA to ClassB or both…
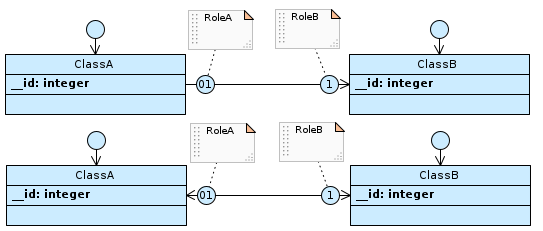
…table ClassA has the foreign key to ClassB, with not null and uniqueness constraints defined.
One-to-one: modeling not allowed #
Since RoleB is not accessible, the following associations cannot be modeled because the navigability conditions do not allow the creation of instances of ClassA:
- associations where the cardinality of
RoleAis01and that ofRoleBis1, navigable fromClassBtoClassA.
The following associations cannot be modeled due to the egg-chicken problem between ClassA and ClassB: it is not possible to define an instance of one in the absence of at least one instance of the other:
- associations where the cardinality of
RoleAis1and that ofRoleBis1, regardless of navigability.
Many-to-many associations #
If the cardinality of RoleA is 0N (* in Designer) and that of RoleB is 0N (* in Designer), regardless of navigability…
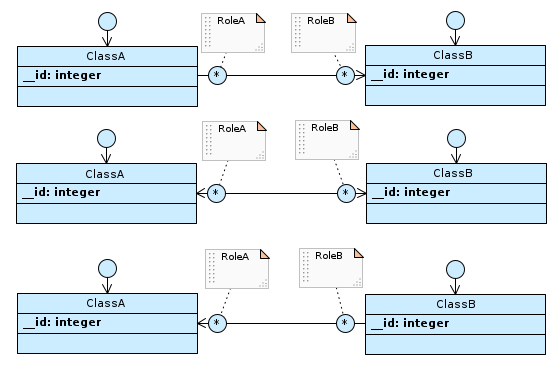
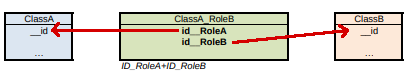
…a relation table named ClassA_RoleB is generated, which has the foreign key to ClassA and ClassB. The respective columns are not null and a unique constraint is defined on the combination of both.
If the cardinality of RoleA is 0N (* in Designer) and that of RoleB is nN (C in Designer), and the association is navigable from ClassA to ClassB or both…
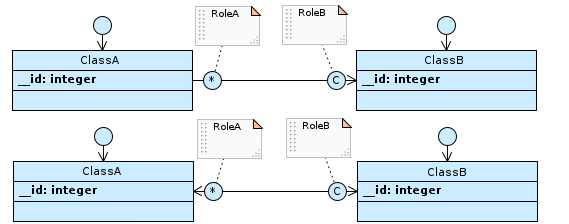
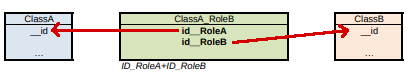
…a relation table named ClassA_RoleB is generated, which has the foreign key to ClassA and ClassB. The respective columns are not null and a uniqueness constraint is defined on the combination of both.
Many-to-many: modeling not allowed #
Since RoleB is not accessible, the following associations cannot be modeled because the navigability conditions do not allow the creation of instances of ClassA:
- associations where the cardinality of
RoleAis0N(*in Designer) and that ofRoleBisnN(Cin Designer), navigable fromClassBtoClassA.
The following associations cannot be modeled because of the egg-chicken problem between ClassA and ClassB: it is not possible to define an instance of one in the absence of at least one instance of the other:
- associations where the cardinality of
RoleAisnN(Cin Designer) and that ofRoleBisnN(Cin Designer), regardless of navigability.
Compositions #
Compositions towards to-one parts…
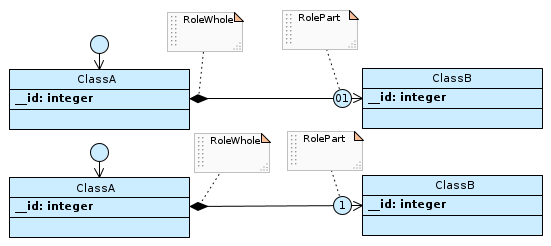
…are rendered with the foreign key in the part table to the whole table. The related column has a unique constraint.

Compositions towards to-many parts…
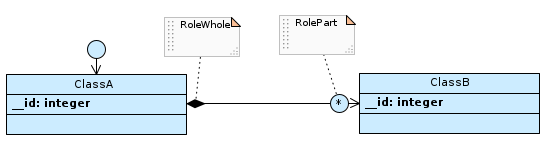
…are rendered with the foreign key in the part table to the whole table, with no constraints defined on the related column.

